Such tubes are mainly used when this level of nutritional support is expected to be a short-term requirement, or when the physical condition of the patient makes it inadvisable for a more intrusive procedure.
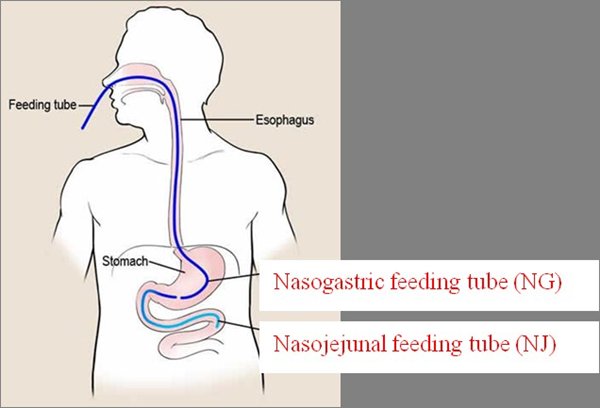
Insertion is achieved by feeding the tube through the nasal cavity and advancing the tube down the back of the throat and the oesophagus until it reaches the stomach, this is known as Naso Gastric (NG). In certain cases it is necessary to advance the tube into the small bowel; the jejunum and known as a naso-jejunal (NJ) tube.
Due to the potential for displacement of the internal end of Nasoenteric tubes without obviously visual indicators patients requiring NG or NJ feeding are required to check the position of their tube before administrating water, feed or drugs through the tube. This is done through the aspirate of a small amount of gastric or jejunal content from the tube and testing the acidity on CE marked pH indicator paper. A pH of <5.5 indicates gastric positioning and pH 6-8 indicates presence in the small bowel.
.aspx)
The feed can be administered using various methods:
BOLUS
Administers the feed solution over a 15-20 minute period, often via a syringe, several times a day; frequently in 150-200ml each session.
INTERMITTENT GRAVITY DRIP
Administers a set volume over 30-60 minutes several times a day, often by a given set only.
CONTINUOUS
Administers the full feed solution over a period of 8-24 hours, often using an enteral feeding pump set to a prescribed rate.
These methods can be used in combination and allow increased flexibility with the feeding regime to met the requirements of the patient. Despite the method used the “Clean Procedure” is always adopted when the tube is connected to the bag / bottle of feed solution.
NJ feeders ONLY will find that there is less flexibility with the methods of administration of the feed. This is primarily due to the fact that the feed solution is administered directly into the small bowel. The stomach acts as a reservoir and therefore is able to hold larger volumes without complications. The small bowel does not have this ability and overloading is a potential risk which can result in vomiting and “dumping syndrome” For this reason, continuous NJ feeders will find the flow rate of the feed is lower than most NG feeders and Bolus NJ feeders will only be able to Bolus smaller volumes.